
How Do Fleet Tracking Telematics Work?
Fleet telematics combines GPS technology, onboard sensors and wireless communications to collect and transmit vehicle data in real time.
A telematics device installed in the vehicle gathers information on location, speed, fuel use, engine performance and driver behaviour.
This data is sent via mobile or satellite networks to a central software platform, where it can be analysed by fleet managers.
By integrating GPS positioning with diagnostic and behavioural information, telematics provides a more complete picture of fleet performance than GPS tracking alone.

What Types of Data Are Collected Through Telemetrics?
Telematics systems can collect a wide range of data, from basic location and speed to more advanced metrics such as fuel efficiency, tyre pressure, braking patterns and engine fault codes.
Some systems also monitor temperature for refrigerated transport or record the operation of specialist equipment.
This detailed information allows managers to identify inefficiencies, schedule maintenance more accurately and improve driver safety.

What are the Benefits of Telematics for Fleets?
Telematics provides benefits across multiple areas of fleet management. It helps reduce costs by optimising routes, improving fuel efficiency and enabling preventative maintenance.
Safety is improved through monitoring and correcting risky driving behaviours.
Telematics also simplifies compliance with regulations by automatically recording driver hours, inspections and emissions data.
The insights gained from telematics data can lead to better decision-making and long-term operational improvements.
Why Choose Telematics vs Just GPS Tracking?
While GPS tracking focuses primarily on vehicle location and movement, telematics adds layers of operational and diagnostic data.
GPS tracking might tell you where a vehicle is and how fast it is travelling, whereas telematics can also reveal how efficiently it is being driven, whether maintenance is due and if there are any mechanical issues.
Telematics offers a broader, more detailed view of fleet performance, making it a valuable upgrade for businesses that want deeper operational insights.
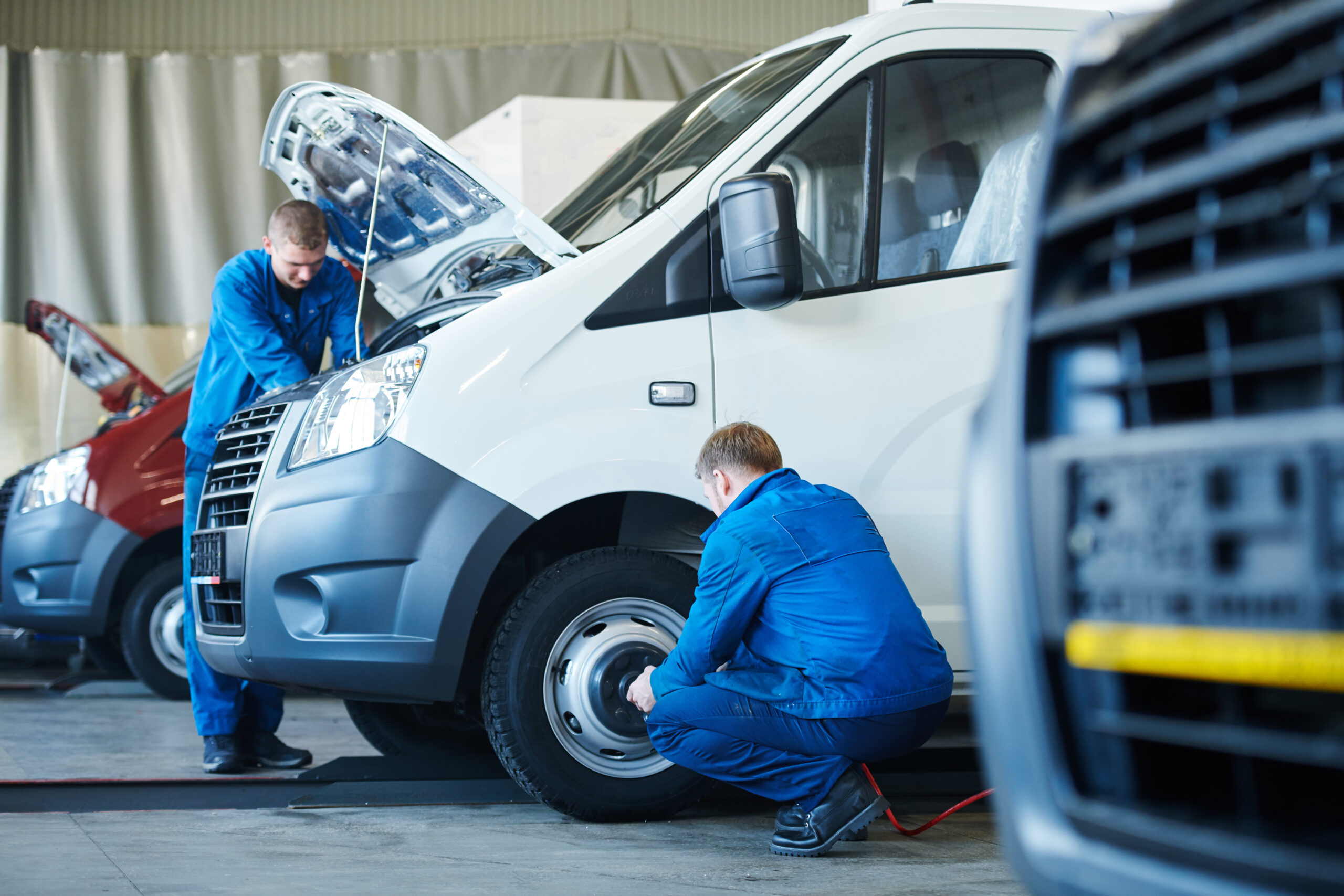

Can I use Telematics for Maintenance Scheduling?
Telematics can track engine performance, mileage, oil life and other maintenance indicators, enabling a proactive approach to servicing.
Automated alerts notify managers when a vehicle needs attention, reducing the risk of breakdowns and costly repairs.
Maintenance schedules can be based on actual usage rather than fixed intervals, ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
Over time, this approach extends vehicle lifespan and improves reliability.

Can Fleet Telemetrics be Used for Environmental Monitoring?
By tracking fuel consumption, emissions and idling time, telematics helps fleets measure and reduce their environmental impact.
Reports can highlight areas where fuel efficiency can be improved, such as route changes or driver training.
Some systems can even track the performance of electric or hybrid vehicles, providing insights into battery usage and charging patterns.
This data supports sustainability goals and helps meet environmental regulations.

Can Telematics be Used for Driver Training?
Telematics provides objective data on driving habits, which can be used to support targeted training programmes.
Managers can identify behaviours such as speeding, harsh braking or excessive idling and work with drivers to improve their performance. Real-time alerts also allow for immediate feedback, helping to reinforce good habits and correct unsafe practices. Over time, this can lead to safer, more efficient driving across the fleet.

Are There Industry-Specific Uses of Telemetrics?
Different industries use telematics in unique ways.
- Logistics companies rely on it for route planning and delivery tracking.
- Construction fleets use it to monitor equipment usage and location.
- Public transport operators track service schedules and passenger safety.
- Refrigerated transport businesses monitor cargo temperatures to maintain product quality.
Tailoring telematics features to industry needs maximises its value and impact.

Is There Data Privacy in Telematics?
Because telematics collects detailed location and behavioural data, protecting privacy is essential.
Businesses must comply with data protection laws such as UK GDPR, ensuring that information is stored securely and accessed only by authorised personnel.
Clear policies should be in place to explain how data is used and to reassure drivers about privacy concerns.

What Is The Future of Telematics?
Telematics is expected to become even more advanced with the integration of artificial intelligence, predictive analytics and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies.
Future systems may offer even greater automation, from predictive maintenance to fully optimised route planning based on live conditions.
As electric and autonomous vehicles become more common, telematics will play a central role in managing and monitoring their performance.